Root cause analysis (RCA) is a methodical approach used to identify the fundamental reasons behind problems failures or undesirable events. It goes beyond simply fixing symptoms and focuses on uncovering the deep-rooted issues that cause them.
By understanding and addressing the root cause organizations and individuals can prevent recurring problems and improve overall efficiency.
What is Root Cause Analysis?
Root cause analysis is a structured technique for identifying the underlying causes of problems or issues. It’s commonly used in industries such as manufacturing healthcare engineering and service industries but its principles can be applied universally.
The idea is to avoid quick fixes or superficial solutions that merely address the symptoms of a problem and instead identify the root cause to implement lasting improvements.
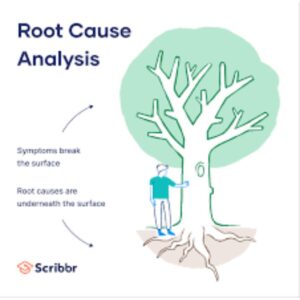
Root cause analysis is often visualized as a method of drilling down through layers of symptoms to uncover the deepest, most fundamental cause. These layers are sometimes referred to as the “5 Whys asking why repeatedly until the core issue is uncovered.
The Importance of Root Cause Analysis
- Prevents Recurrence
One of the key reasons for conducting root cause analysis is to prevent the same problem from recurring. If you only fix the visible symptoms, you may experience the same problem again in the future. By identifying and eliminating the root cause, you ensure that the problem does not resurface. - Improves Processes
Root cause analysis is not just about fixing problems; it’s also about improving systems and processes. By discovering why something went wrong, you can refine processes, reduce inefficiencies, and enhance performance in the long term. - Saves Time and Resources
Addressing the root cause of a problem often saves time and resources in comparison to repeatedly fixing symptoms. Organizations can avoid wasting effort on temporary fixes and instead focus on long-term solutions that address the core issue. - Promotes a Culture of Continuous Improvement
When root cause analysis is done properly, it fosters a culture of learning and continuous improvement within organizations. It encourages people to ask questions, explore deeper issues, and make data-driven decisions.
Steps Involved in Root Cause Analysis
Effective root cause analysis typically involves several key steps:
1. Define the Problem
The first step is to clearly define the problem. What happened, and when did it happen? This will give you a clear starting point for the analysis.
2. Collect Data
Next, gather relevant data. This includes both qualitative and quantitative data, such as reports, observations, interviews, and logs. The goal is to understand the context and scope of the problem.
3. Identify Possible Causes
Once you have a clear understanding of the problem, brainstorm all possible causes. This step involves asking “why” multiple times (as mentioned in the “5 Whys” method) to drill down and identify potential root causes. Look for patterns, correlations, and any anomalies that could point to the underlying issues.
4. Analyze the Causes
After identifying potential causes, it’s time to analyze them. This could involve looking for common factors, conducting tests or experiments, or mapping out cause and effect relationships.
Root cause analysis tools, such as fishbone diagrams or Pareto charts, can be useful during this phase.
5. Implement Solutions
Once the root cause has been identified, the next step is to implement solutions. These solutions should be aimed at addressing the core problem, not just alleviating its symptoms.
Whether it’s a process change, policy revision, or technical upgrade, the solution should tackle the root cause head on.
6. Monitor and Follow-Up
Continuous monitoring allows you to catch any new issues early and take corrective action if needed.
Techniques and Tools for Root Cause Analysis
There are several techniques and tools that can be used in the process of root cause analysis. These tools help visualize and analyze potential causes, making the analysis process more efficient.
- 5 Whys
As mentioned earlier, the 5 Whys technique involves asking “why” repeatedly to drill down to the root cause of a problem. It is a simple yet effective tool for identifying the underlying cause without making assumptions. - Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa Diagram)
A fishbone diagram is a graphical tool that helps identify potential causes of a problem in various categories, such as people, processes, equipment, materials, and environment. - Pareto Analysis
Based on the 80/20 rule, Pareto analysis helps identify the most significant causes of a problem by focusing on the factors that contribute the most to the issue. - Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
FMEA is a systematic method for evaluating potential failure modes in a system, process, or product and identifying their causes. This tool is particularly useful in engineering and manufacturing settings to anticipate problems before they occur.Also Read: Alpine Investors
Common Applications of Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis can be applied in various sectors, including:
- Manufacturing
In manufacturing, RCA is used to identify the causes of product defects, machinery failures, and production delays. By performing roots cause analysis, manufacturers can enhance quality control, reduce downtime, and improve production efficiency. - Healthcare
In healthcare settings, roots cause analysis helps identify the causes of medical errors, patient safety incidents, or inefficiencies in care delivery. This is critical for improving patient outcomes and optimizing healthcare practices. - Business and Operations
Businesses use roots cause analysis to improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and streamline processes. By identifying bottlenecks, miscommunications, or ineffective practices, businesses can improve their workflows and increase profitability. - Information Technology (IT)
In IT roots cause analysis is used to troubleshoot technical issues, such as network outages, software bugs or system failures. By identifying the root cause of IT problems, teams can implement more effective solutions and improve system stability.
Challenges in Root Cause Analysis
While roots cause analysis is an invaluable tool, it comes with its own set of challenges. These include:
- Lack of Data
In some cases, insufficient or inaccurate data can hinder the analysis process. It’s essential to gather accurate and complete data to effectively identify the root cause. - Bias and Assumptions
Analysts may be prone to making assumptions or focusing on obvious causes without fully exploring deeper issues. Avoiding cognitive bias is critical in ensuring the integrity of the analysis. - Complex Problems
Some problems are multifaceted and involve multiple root causes. In such cases, it can be difficult to pinpoint a single cause. It’s important to break down complex problems and tackle each contributing factor separately.
Final Thoughts Of Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis is an essential technique for uncovering and addressing the true causes of problems. Whether in manufacturing, healthcare, business, or IT applying RCA can lead to lasting improvements and prevent recurring issues.
By following a systematic approach, utilizing proven tools, and overcoming challenges organizations can identify root causes with precision and implement solutions that drive long term success.
By prioritizing root cause analysis in your problem solving processes, you can enhance efficiency, improve processes and create a culture of continuous improvement within your organization or personal life. Roots cause analysis isn’t just about solving problems.